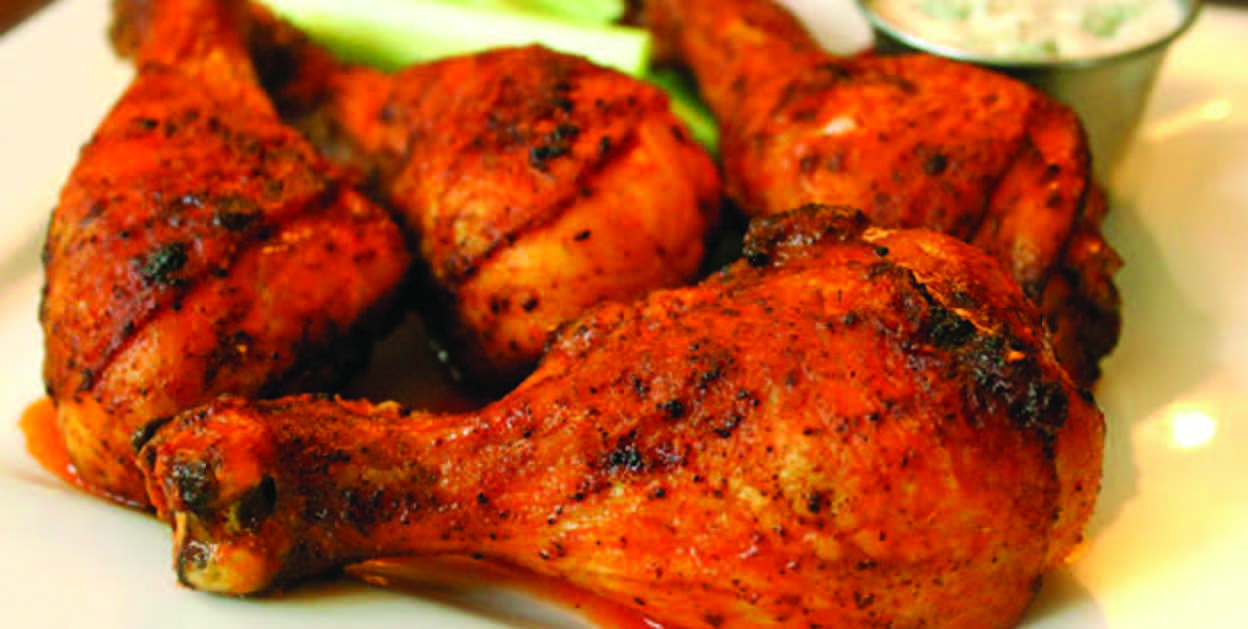

Each time you eat chicken, you could also be consuming a cocktail of antibiotics. A lab study released by Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) found antibiotic residues in 40% of chicken samples bought from outlets in Delhi and NCR. Antibiotics are substances that can destroy or inhibit the growth of micro-organisms. They are widely used in prevention and treatment of infectious diseases.
1: Six antibiotics tested from there antibiotic classes – tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones and aminoglycosides.
2: Each chicken sample analyzed thrice.
3: Antibiotics found in all tissues tested- muscles, liver and kidney.
4: No significant difference in residues in different parts of chicken. 5: More than on antibiotic found in 17% chickens.
Why this could be dangerous?
1: Banned in certain countries for use in animals due to concerns about antibiotic resistance (Enrofl oxacin and Ciprofl oxacin).
2: Considered critical (ciprofl oxacin) and highly important (tetracyclines) for humans. 3: Among the highest prescribed in India (ciprofl oxacin).
Why antibiotics are given to chicken?
1: Because this cheap input has a growth promoting effect, making the chicken look fatter.
2: Due to unsanitary conditions in poultry, chickens contract bacterial infections that require treatment antibiotics.
3: Antibiotic for feed is freely available at a low cost in Delhi and outside.
4: Raw chicken has more antibiotic residue than cooked chicken.
5: Regularly exposing yourself to antibiotics through chicken will lead to resistance to some of the important and common antibiotics.
Prevalence of antibiotic resistance? In US:
2 million illnesses and 23,000 deaths annually; estimated $ 20 billion as direct annual healthcare cost. In EU: 25,000 deaths and about Euro 1.5 billion of healthcare cost & productivity losses.
In India (no national level estimate): About one-third of two lakh children that die in the fi rst four weeks are victims of antibiotic resistance; about 15% of those re-treated for TB are resistant to multiple drugs.
What about regulations
India has no regulations or standards for antibiotics given to farm animals.
Some European countries banned use of penicillin, streptomycin and tetracyclines as growth promoters in 1970s. In 1986, Sweden banned antibiotic growth promoters and Denmark followed it.
EU prohibited antibiotic growth promoters in 2006. Between 1995 and 2008, Denmark’s strong policies led to reduction in antibiotic usage by 90% in poultry and 51% in pigs. USA’s voluntary approach a failure. About 80% of antibiotics used in food-producing animals. In 2009-11, use of lincosamides, penicillins and tetracyclines grew by 64%, 44% and 22%, respectively.




Be the first to comment